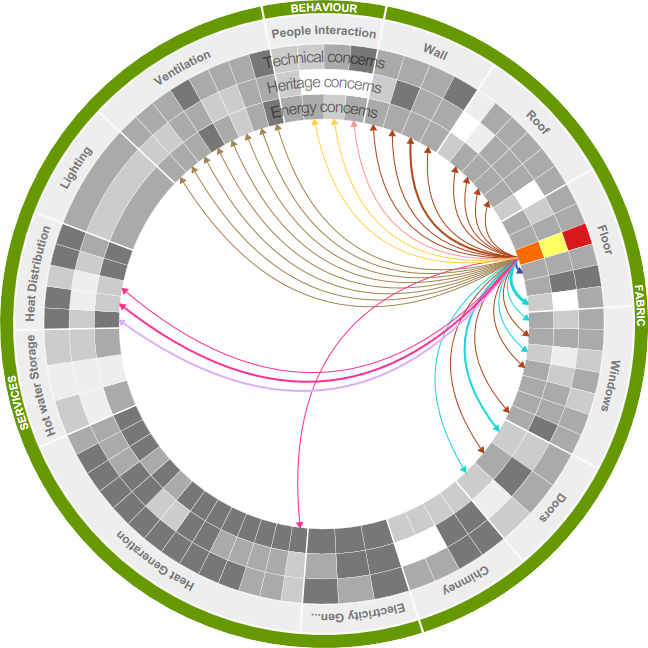
Concern & action: Relation to Building Thermal Performance
Need for an accurate understanding of the heating demand in order to correctly specify the energy system. Incorrect understanding can lead to wasteful or inadequate system specification.
Suggested actions
Before Implementation
Undertake in situ measurements and tests to establish whole building performance. e.g. air pressure test, room condition monitoring, U-value measurement etc. Undertake whole building energy numerical modelling (i.e. IES, Energy Plus etc.) using measured in situ data within model in order to make a thorough assessment of all contributory factors to energy performance and building heat demand. Improve fabric thermal performance and airtightness before installation of any low temperature heating system.
During implementation
Match the design heat demand to the proposed heating system rating. Avoid oversizing of heating system to maximise efficiency and coefficient of performance of system.
After implementation
Monitor 'as improved' results and building performance in operation and feedback results to add to knowledge of actual performance of buildings in use.
RELATED MEASURES
 SERVICES (11)
SERVICES (11)
High efficiency gas-fired condensing boilers
Oil-fired condensing boilers
Air source heat pumps
Ground/Water source heat pumps
Biomass boilers
Biomass stove with back boiler
Fan-assisted replacement storage heaters
Communal heat generating system
Micro combined heat and power
High efficiency replacement warm-air units
RELATED REFERENCES (5)
Performance and control of domestic ground-source heat pumps in retrofit installations (2011)
Boait, P.J., Fan, D. and Stafford, A.
Detailed analysis from the first phase of the Energy Saving Trust’s heat pump trial (2012 )
Dunbabin P and Wickins C
Micro CHP Accelerator - final report (CTC788) (2011)
Guy,R. and Sykes,B.
Getting Warmer: a field trial of heat pumps (2010)
Energy Saving Trust